Free Cooling Air Conditioning
What is free cooling and how can it reduce Air Conditioning operational costs? Free cooling provides significant opportunities to generate energy savings. It can take effect when the difference between the outside supply and return temperatures is as little as 1°C. This means that, in a 24/7 data centre with a typical room temperature of 24°C, over 95% of the year can be spent with free-cooling active.
Concurrent free cooling In addition to energy savings through reducing the need for mechanical (DX) cooling, concurrent free-cooling also maximises the part-load efficiencies of components such as EC fans, inverter-driven pumps and centrifugal compressors. The variable speed control on such components allows load to be very precisely matched to cooling duty, reducing energy consumption and unnecessary wear. EC fans for example are up to 70% more efficient than AC fans at part-load. 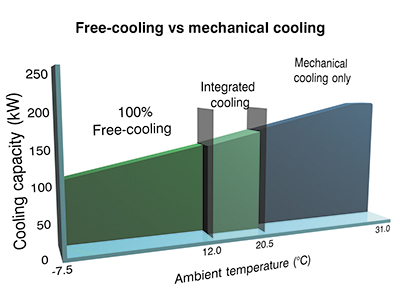
The use of temperature sensors and sequencer controls allows for cooling to be staged, ensuring a smooth transition from mechanical cooling to air free cooling.
On sites with an air cooled and free cooling chiller, the sequencer ensures that when the ambient is low, the free cooling chiller is the first to start up.
In terms of the costs of ownership, energy represents by far the biggest item of expenditure, often outweighing the initial capital costs over the course of a unit`s lifetime; in the case of a traditional DX computer room air conditioning (CRAC) system, estimated energy costs over the course of five years can add up to 5 or 6 times the initial cost of the unit. Free cooling units can easily pay for themselves within the first 1 to 2 years and, by the end of five years, total costs of ownership can equate to around half those of DX systems. Free cooling opportunities can therefore make a significant saving on operational budgets, generating PUEs of 1.1 or below.
 Rooftop Packaged Unit
Rooftop Packaged Unit Water Chiller
Water Chiller